Silicone Hydrogel Lenses
The development of contact lenses
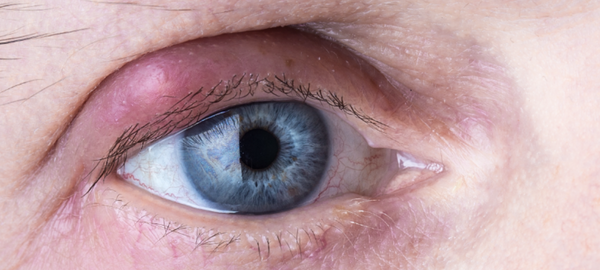
Arguably the main preoccupation of contact lens developers over the years has been increasing oxygen permeability. If worn for an extended period of time, traditional contact lenses deprive the cornea of much-needed oxygen. Without adequate oxygen, the cornea dries out and can become inflamed, which is a condition known as keratitis. This can cause itchiness and pain, and in more severe cases, can impair vision and lead to long-term damage such as scarring. In the quest to find a longer lasting, comfortable contact lens, the ability to improve oxygen permeability is crucial. Thus, silicone hydrogel contact lenses have been a game-changer for all contact lens wearers.
Silicone Hydrogel
Soft contact lenses were first created in the 1960s, after the development of ‘hydrophilic gels’ or hydrogels. Problems of keratitis became more widespread with the introduction of extended wear contact lenses in the 90s because more people were wearing contact lenses for longer periods of time. This resulted in many people getting infections.
The first silicone hydrogel contact lenses were introduced to the public in 1999. This amazing new technology allowed up to seven times more oxygen to reach the cornea compared to traditional hydrogel lenses, meaning that for the first time extended wear contact lenses did not lead to an increased health risk.
Oxygen permeability
The higher permeability of silicone means that the oxygen permeability of silicone hydrogel lenses is not tied to the amount of water in the lens. For the wearer, this means increased comfort, and the ability to wear the lenses continuously for an extended period of time. Studies have also shown that any infections that do occur tend to be less severe than with traditional Hydrogel lenses.
Contact lenses for dry eyes
Whilst they are not perfect, there is no denying that Silicon Hydrogel represents a major step forward in contact lens technology, and it is no coincidence that the market has been heading in this direction for some years now. Whilst they may not be for everyone, almost any contact lens wearer is in a position to try them out, though we will always recommend that you consult your optician before switching your contact lenses. People who stand to benefit the most from Silicone Hydrogel contact lenses are those who tend to wear their lenses for more than twelve hours a day, particularly if they spend a lot of time in low humidity environments (offices with air-conditioning is one example of this). Patients with high prescriptions, or younger people who haven’t yet got the hang of their contact lens wear and maintenance routine, will also benefit, as will anyone who regularly experiences dryness, redness, or any other discomfort towards the end of a day wearing traditional contact lenses.
Silicone Hydrogel Contact lenses come in a variety of brands and different duration of wear. Many Silicone Hydrogel lenses have been approved for overnight wear for up to seven nights, and there are even pairs that can be worn for up to 30 nights continuously.
How to choose the right contact lenses
What are the differences between daily and monthly contact lenses? Choosing the right contact lenses for your needs comes down to two main things, your prescription and lifestyle.
Daily contact lenses are typically thinner than monthly contact lenses and have high water content. 1 day silicone hydrogel contact lenses should for example be word for around 12 hours a day and then removed overnight to let the eyes rehydrate. Residue from the eye easily build up and affects the quality of the lens. Therefore, daily contacts should be disposed of and not reused after wearing them. If you play sports or engage in outdoor activities, daily contact lenses may be the better option for you as the lenses are likely to be exposed to dirt and can be replaced daily.
Monthly lenses are thicker and durable, making them more long-lasting. They do not dry out as easily if properly taken care of and stored and can therefore be reused multiple times. Your vision correction needs is important when choosing contact prescription lenses. Since monthly contact lenses are made with a harder composition, they are more suitable for prescriptions that require higher magnification. If you have a complex prescription, monthly lenses are typically more suitable for you.
If you have sensitive or dry eyes, silicone hydrogel contact lenses are a good option and together with your eye doctor you can discuss the perfect fit for your needs.
At SmartBuyGlasses, we stock a wide range of the leading brands of silicone hydrogel lenses, including Acuvue Oasys, PureVision 2 and Air Optix. Check out all the silicone hydrogel lenses available on our website here.
Silicone Hydrogel Lenses
The development of contact lenses
Arguably the main preoccupation of contact lens developers over the years has been increasing oxygen permeability. If worn for an extended period of time, traditional contact lenses deprive the cornea of much-needed oxygen. Without adequate oxygen, the cornea dries out and can become inflamed, which is a condition known as keratitis. This can cause itchiness and pain, and in more severe cases, can impair vision and lead to long-term damage such as scarring. In the quest to find a longer lasting, comfortable contact lens, the ability to improve oxygen permeability is crucial. Thus, silicone hydrogel contact lenses have been a game-changer for all contact lens wearers.
Silicone Hydrogel
Soft contact lenses were first created in the 1960s, after the development of ‘hydrophilic gels’ or hydrogels. Problems of keratitis became more widespread with the introduction of extended wear contact lenses in the 90s because more people were wearing contact lenses for longer periods of time. This resulted in many people getting infections.
The first silicone hydrogel contact lenses were introduced to the public in 1999. This amazing new technology allowed up to seven times more oxygen to reach the cornea compared to traditional hydrogel lenses, meaning that for the first time extended wear contact lenses did not lead to an increased health risk.
Oxygen permeability
The higher permeability of silicone means that the oxygen permeability of silicone hydrogel lenses is not tied to the amount of water in the lens. For the wearer, this means increased comfort, and the ability to wear the lenses continuously for an extended period of time. Studies have also shown that any infections that do occur tend to be less severe than with traditional Hydrogel lenses.
Contact lenses for dry eyes
Whilst they are not perfect, there is no denying that Silicon Hydrogel represents a major step forward in contact lens technology, and it is no coincidence that the market has been heading in this direction for some years now. Whilst they may not be for everyone, almost any contact lens wearer is in a position to try them out, though we will always recommend that you consult your optician before switching your contact lenses. People who stand to benefit the most from Silicone Hydrogel contact lenses are those who tend to wear their lenses for more than twelve hours a day, particularly if they spend a lot of time in low humidity environments (offices with air-conditioning is one example of this). Patients with high prescriptions, or younger people who haven’t yet got the hang of their contact lens wear and maintenance routine, will also benefit, as will anyone who regularly experiences dryness, redness, or any other discomfort towards the end of a day wearing traditional contact lenses.
Silicone Hydrogel Contact lenses come in a variety of brands and different duration of wear. Many Silicone Hydrogel lenses have been approved for overnight wear for up to seven nights, and there are even pairs that can be worn for up to 30 nights continuously.
How to choose the right contact lenses
What are the differences between daily and monthly contact lenses? Choosing the right contact lenses for your needs comes down to two main things, your prescription and lifestyle.
Daily contact lenses are typically thinner than monthly contact lenses and have high water content. 1 day silicone hydrogel contact lenses should for example be word for around 12 hours a day and then removed overnight to let the eyes rehydrate. Residue from the eye easily build up and affects the quality of the lens. Therefore, daily contacts should be disposed of and not reused after wearing them. If you play sports or engage in outdoor activities, daily contact lenses may be the better option for you as the lenses are likely to be exposed to dirt and can be replaced daily.
Monthly lenses are thicker and durable, making them more long-lasting. They do not dry out as easily if properly taken care of and stored and can therefore be reused multiple times. Your vision correction needs is important when choosing contact prescription lenses. Since monthly contact lenses are made with a harder composition, they are more suitable for prescriptions that require higher magnification. If you have a complex prescription, monthly lenses are typically more suitable for you.
If you have sensitive or dry eyes, silicone hydrogel contact lenses are a good option and together with your eye doctor you can discuss the perfect fit for your needs.
At SmartBuyGlasses, we stock a wide range of the leading brands of silicone hydrogel lenses, including Acuvue Oasys, PureVision 2 and Air Optix. Check out all the silicone hydrogel lenses available on our website here.